Blog
How to Determine Distance and Time to the Point of Equal Time and Point of Safe Return
- March 8, 2024
- Posted by: admin2139
- Category: Education

Determining the distance and time to the Point of Equal Time (PET) involves finding the location along your flight route where the time required to reach your destination matches the time needed to turn around and return home. The formulas for Distance to the Point of Equal Time (DPET) and Time to the Point of Equal Time (TPET) are outlined below, accounting for groundspeed variations due to wind.
Distance to the Point of Equal Time (DPET)
To find DPET, you will need:
- Total distance from your origin to destination (D)
- Ground speed home (GSH)
- Groundspeed out (GSO)
Example:
- D = 560 NM
- GSH = 180 KTS
- GSO = 220 KTS

Time to the Point of Equal Time (TPET)
To determine TPET, you need:
- Distance to the Point of Equal Time (DPET)
- Groundspeed out (GSO)
Example:
- DPET = 252 NM
- GSO = 220 KTS
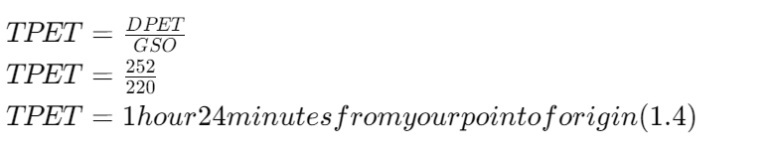
Calculating Time and Distance to Point of Safe Return (PSR)
The Point of Safe Return (PSR) marks the location on your flight route where you can still return to your origin based on endurance. The formulas for Time to Point of Safe Return (TPSR) and Distance to Point of Safe Return (DPSR) are outlined below.
Time to Point of Safe Return (TPSR)
To calculate TPSR, you will need:
- Endurance (E)
- Ground speed home (GSH)
- Groundspeed out (GSO)
Example:
- E = 5 hours
- GSH = 180 KTS
- GSO = 220 KTS
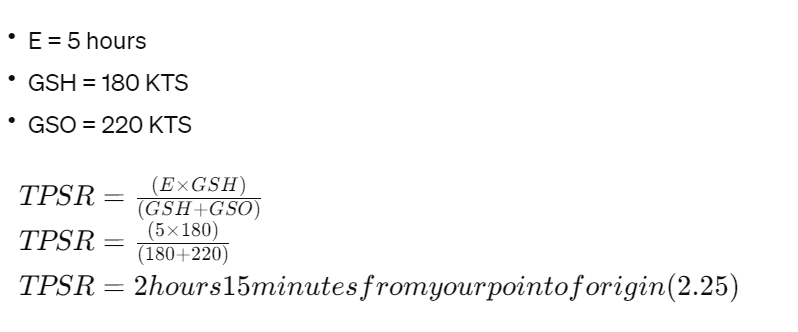
Distance to Point of Safe Return (DPSR)
To find DPSR, you need:
- Time to Point of Safe Return (TPSR)
- Groundspeed out (GSO)
Example:
- TPSR = 2.25 hours
- GSO = 220 KTS

