Blog
Understanding the Procedures for Altimeter Setting in Aviation
- March 5, 2024
- Posted by: admin2139
- Category: Education
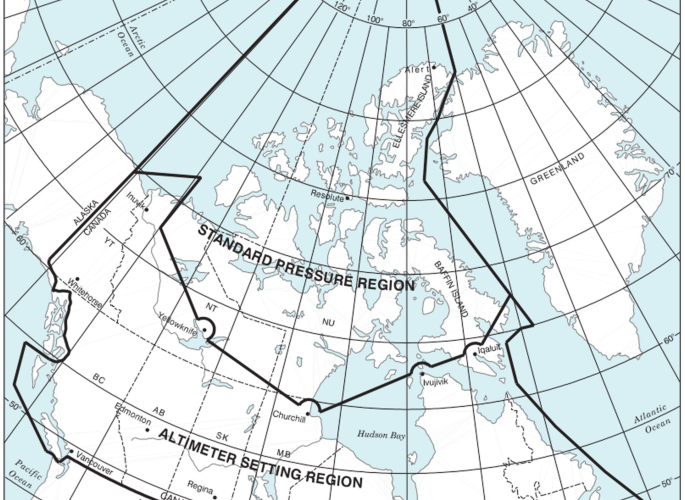
The precise operation of an aircraft requires strict compliance with a range of regulations, particularly those governing altimeter setting procedures. These procedures play a pivotal role in maintaining accurate altitude readings and ensuring the safety of flight operations. Let’s explore the specific guidelines outlined for altimeter setting in both the altimeter setting region and the standard pressure region.
Altimeter Setting Region Within the altimeter setting region, covering dimensions below 18,000 feet ASL, pilots must follow specific altimeter setting procedures at different stages of flight.
Departure Prior to takeoff, pilots must adjust the aircraft altimeter to the current altimeter setting of the aerodrome. If this information is unavailable, setting it to the aerodrome’s elevation becomes necessary.
En route During the flight, the altimeter should be set to the current altimeter setting of the nearest station along the route. If stations are more than 150 NM apart, the setting of a station near the route should be used.
Arrival Approaching the intended landing aerodrome requires setting the altimeter to the current aerodrome altimeter setting, if available.
Standard Pressure Region Above 18,000 feet ASL and in low-level airspace outside the lateral limit of the altimeter setting region, the standard pressure region comes into effect, bringing distinct flight procedures.
General Operating an aircraft within the standard pressure region requires setting the altimeter to standard pressure: 29.92 inches of mercury or 1013.2 mbs.
Departure Before takeoff, pilots set the altimeter to the current altimeter setting of the aerodrome or, if unavailable, to the aerodrome’s elevation. Upon reaching the planned cruising flight level, it should be set to standard pressure.
Arrival Descending for landing requires setting the altimeter to the current altimeter setting of the intended landing aerodrome, if available. Adjustments are made based on specific procedures during holding or descent from cruising flight levels above FL 180.
Transition Procedures Transiting between regions necessitates careful consideration of altimeter settings, as specified in CAR 602.37. Pilots must make altimeter setting changes while within the standard pressure region before entering or after leaving the altimeter setting region.
In conclusion, strict adherence to altimeter setting procedures is crucial for ensuring safe flight operations. Pilots must acquaint themselves with these regulations to guarantee precision and accuracy in altitude readings throughout all flight phases.
Additional Resources for Altimeter Settings For more comprehensive information on altimeter setting procedures and flight regulations, pilots are encouraged to consult CARs 602.35 and CARs 602.36. Additionally, valuable insights can be found in the Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) section RAC—Rules Of The Air And Air Traffic Services 2.10. These resources provide detailed guidelines and essential knowledge to ensure compliance with altimeter setting protocols and safe flight operations in various airspace regions.
